The 5 Circles
"The Problem of Jiang Zemin" (Former Chinese President).
It is said that he used to confront mathematicians as well as school children
with this problem.
Gegeben ist ein nicht-konvexes Fünfeck: fünf Dreiecke ragen
heraus. Die Umkreise benachbarter Dreiecke schneiden sich in zwei
Punkten: einer dieser Schnittpunkte liegt auf zwei der Geraden
- uns interessiert jeweils
der zusätzliche Schnittpunkt: Insgesamt erhalten wir fünf
solche Schnittpunkte und es gilt: Sie liegen auf einem Kreis.
The General Result: Lines in the Plane
Theorem.
Let L be a finite set of lines in the plane of cardinality |L| at least 2
and assume that they are in general position.
- If |L| is even, these lines determine a point P(L),
- If |L| is odd, they determine a circle C(L),
with the following property:
- For |L| = 2, P(L) is the intersection of the two lines.
Assume now that |L| is at least 3 and that L' is obtained from L by deleting one line. Then:
- If |L| is even, then C(L') passes through P(L).
- If |L| is odd, then P(L') lies on C(L).
Of course, one can use the properties in order to construct inductively
P(L) and C(L), respectively; in particular P(L) and C(L) are uniquely determined.
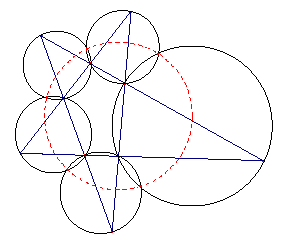
The case n=5: The pentagon picture above exhibits some of the circles and points:
given
is a set L of five lines,
- the red circle is C(L),
- the black circles are some of the circles C(L''), where L'' is a
triple of lines.
- the intersection of the red circle with the black ones are the points
P(L'), with L' being a quadruple of lines.
- (One could add another 5 black circles by looking at the remaining triples
of lines, any one of these would pass through two of the points P(L').)
References: W.K.Clifford: Synthetic proof of Miquel's theorem.
in Mathematical Papers, Macmillan 1882.
I. Yaglom: Complex Numbers in Geometry. Academic Press 1968.
In particular, see:
Probleme des 5 cercles
(with a link to a file (ps and pdf) with full proofs, by Thomas Chomette).
See also Clifford's Circle Theorem

