Workshop on Dynamical Systems and Aperiodic Order
Bielefeld University, Germany
14th - 17th March 2011
overview program abstracts
Abstracts of all talks
All talks take place in Room V3-201 ("Common Room") in the Bielefeld University main building. Click here for a description of the main building.
Talks
| Yohji Akama | Epsilon-duals of model sets and diffraction measure of randomized model sets |
| José Aliste-Prieto | Tower systems for linearly repetitive Delone sets |
| Peter Grabner | Erdős measures revisited |
| Laurent Marin | Dynamical bounds for Sturmian operators |
| Peter Müller | Random Schrödinger operators on aperiodic structures |
| Tobias Oertel-Jäger | Quasiperiodically forced circle maps and related systems |
| Laurent Raymond | Constructive gap-labeling and scaling properties of Schrödinger operator with Sturmian potential |
| Christoph Richard | Ergodic properties of randomly coloured point sets |
| Yudai Sakano | Towards classification of spherical tilings by congruent quadrangles |
| Nicolae Strungaru | Almost periodic measures and cut and project schemes |
| Jörg Thuswaldner | Topological properties of self-affine tiles |
| William Yessen | Dynamics of the Fibonacci trace map and some applications to quasiperiodic models |
Epsilon-duals of model sets and diffraction measure of randomized model sets
Yohji Akama
Abstract:Yohji Akama(1) and Shinji Iizuka(2)
(1) Mathematical Institute, Tohoku University.
(2) Research and Development Section, Hitachi East Japan Solutions, Ltd.
By using a dynamical system, we will show following two results:
(1) Moody's epsilon dual of a model set over a cut-and-project scheme with a window W is exactly the model set over the dual cut-and-project scheme with the window being the epsilon-dual of W.
(2) For a random field on a general discrete set, we introduce a condition that the range of the correlation from each site is within a predefined compact set D. For such a random field defined on a model set that satisfies a natural geometric condition, we quantitatively calculate the diffraction measure of the random field.
Tower systems for linearly repetitive Delone sets
José Aliste-Prieto
Abstract:Tower systems are a way of generalizing classical Kakutani Rohlin partitions to the dynamical systems generated by delone sets and tilings. In this talk, we show, following Benedetti, Bellissard and Gambaudo, how to construct tower systems for linearly repetitve Delone sets and show that the associated transition matrices are uniformly bounded in size and norm. Finally, we discuss applications of this construction.
This is joint work with D. Coronel from PUC of Chile.
Erdős measures revisited
Peter Grabner
Abstract:Let
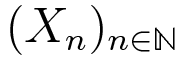 be a sequence of independent random variables
taking values 0 and 1 with equal probability. Erdős in 1939 studied the
distribution of the series
be a sequence of independent random variables
taking values 0 and 1 with equal probability. Erdős in 1939 studied the
distribution of the series
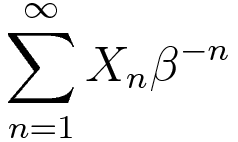
Dynamical bounds for Sturmian operators
Laurent Marin
Abstract:We study the dynamics of discrete, one-dimensional, sturmian Schrödinger operators. We consider H = Δ + V, where Δ is the discrete Laplacian and V is a discrete quasiperiodical function associated to a rotation irrationnal number. The main result is a dynamical bound from above for transport exponents that valuate speed of the wavepacket spreading under time evolution. This bound is true for almost every sturmian potential and is sub-ballistic for a coupling constant big enough. This bound is valid with respect to a full Lebesgue mesure diophantine condition on the irrational number associated to the potential. This condition is true for almost every irrational numbers. We show an example of irrational number with ballistic motion at any coupling constant. We study the fractal dimension of the spectrum of these operators which can bound from below, under more restrictive assumptions, transport exponents. We get a new bound from below for the box dimension of the spectrum.
Random Schrödinger operators on aperiodic structures
Peter Müller
Abstract:Building on a general ergodic theorem for randomly coloured point sets, we establish basic ergodic properties of covariant random operators defined on those point sets. We will concentrate on non-randomness of the spectrum and existence of the integrated density of states. Special attention will be paid to the exclusion of exceptional instances in the case of uniquely ergodic systems.
This is joint work with C. Richard (Erlangen).
Quasiperiodically forced circle maps and related systems
Tobias Oertel-Jäger
Abstract:We give an overview over the theory of quasiperiodically forced circle maps, focusing on a generalization of Poincare's classification of circle homeomorphisms and the consequences of this result for mode-locking phenomena. Some aspects of this theory can be carried over to other areas in topolgical dynamics, including special flows, maps on 1D quasicrystals, almost-periodic scalar differential equations and other dynamical systems arising from hull constructions on the real line.
The talk is a survey about results that have been obtained with various co-authors, in particular with Gerhard Keller, Jaroslav Stark, Kristian Bjerklöv and José Aliste-Prieto.
Constructive gap-labeling and scaling properties of Schrödinger operator with Sturmian potential
Laurent Raymond
Abstract:We consider the class of quasiperiodic Schrödinger operator with so-called step-potential. By means of the trace map, we describe the spectrum by putting it in one-to-one correspondence with a Cantor set of sequences of symbols.
This symbolic representation allows a computation of the integrated density of states for all energies of the spectrum. The identification of the gap-edges leads to the gap labelling of the operator. Namely, the set of gaps of the spectrum is in one-to-one correspondence with the set of relative integers. We also get some insight on the scaling properties of the bands and gaps under the action of the trace-map.
To investigate the dynamical properties of these operators, such as the time-evolution of a wave-packet, a better description of the spectral measure is needed. As a starting point, the golden-mean case, is a good candidate.
In this so-called Fibonacci model, we obtain an upper bound for the Haussdorff dimension of the spectrum. To go one step further, a numerical inversion of the coding function is performed and some scaling properties are shown.
Ergodic properties of randomly coloured point sets
Christoph Richard
Abstract:In order to analyse spectral properties of an aperiodically ordered point set such as the vertex set of the Penrose tiling, it has proven useful to consider the closure of the collection of all translates of the given point set, with respect to a suitable topology. In particular, there is a geometric characterisation of unique ergodicity in terms of so-called uniform pattern frequencies.
We prove such a characterisation within a generalised setup, where we allow for a uniformly discrete point set in a locally compact metric space and a continuous and proper action of a locally compact, metric, unimodular group, which admits suitable averaging sequences.
We will discuss applications of our setup to random colourings and graphs.
This is joint work with Peter Müller, Munich.
Toward classification of spherical tilings by congruent quadrangles
Yudai Sakano
Abstract:Ueno-Agaoka provided an exhaustive classification of spherical tilings by congruent triangles, and proved that for spherical tilings by congruent quadrangles, the proto tile has at least two edges of the same length. In this talk, we are concerned with classifications of spherical tilings by congruent quadrangles. For the spherical tilings by congruent quadrangles that are divided into two congruent triangles, we completed an exhaustive classification by using the Ueno-Agaoka's classification. For the spherical tilings by congruent convex quadrangles that are not divided into two congruent triangles, we completed classification so long as the number of faces are 6 or 8, and generalize the classification for the case the number of faces is even.
Almost periodic measures and cut and project schemes
Nicolae Strungaru
Abstract:In this talk we review the connection between almost periodicity and cut and project formalism and characterize two classes of almost periodic measures in terms of cut and project schemes and continuous functions on the internal space. As a nice application we see that the pure point diffraction measure of any Meyer set can be obtained from a cut and project scheme.
Topological properties of self-affine tiles
Jörg Thuswaldner
Abstract:In this talk we want to survey results on topological properties of self-affine sets. We start with results of Hata on connectivity as well as criteria on arclikeness. In a second part we discuss topological properties of self-affine subsets of the plane. Here the Jordan curve theorem and its consequences allows to give quite simple criteria for the homeomorphy to a disk. In the last part we deal with representations of self-affine fractals as metric projective limits. Together with methods from low dimensional topology such representations enable us to prove topological results on self-affine sets also in higher dimensions.
Dynamics of the Fibonacci trace map and some applications to quasiperiodic models
William Yessen
Abstract:Since the discovery of quasicrystals, quasiperiodic models in mathematical physics have formed an active area of research. The method of the so-called trace maps, originally introduced by M. Kohmoto, L. P. Kadanoff and C. Tang in early '80s, has provided a means for rigorous investigation into the physical properties of one-dimensional quasiperiodic structures, leading, for example, to fundamental results in the spectral theory of discrete Schrodinger operators and Ising models (both classical and quantum) on one-dimensional quasiperiodic lattices. We shall discuss dynamical properties of the so-called Fibonacci trace map - an analytic map on the three-dimensional Euclidean space that arises in the investigation of quasiperiodic models on lattices generated by the Fibonacci substitution rule - and its applications to the spectral theory of discrete quasiperiodic Schrodinger operators and quasiperiodic Ising models.